Hyperglycemia is a condition in which the concentration of glucose in the blood exceeds the normal range.
Common symptoms include:
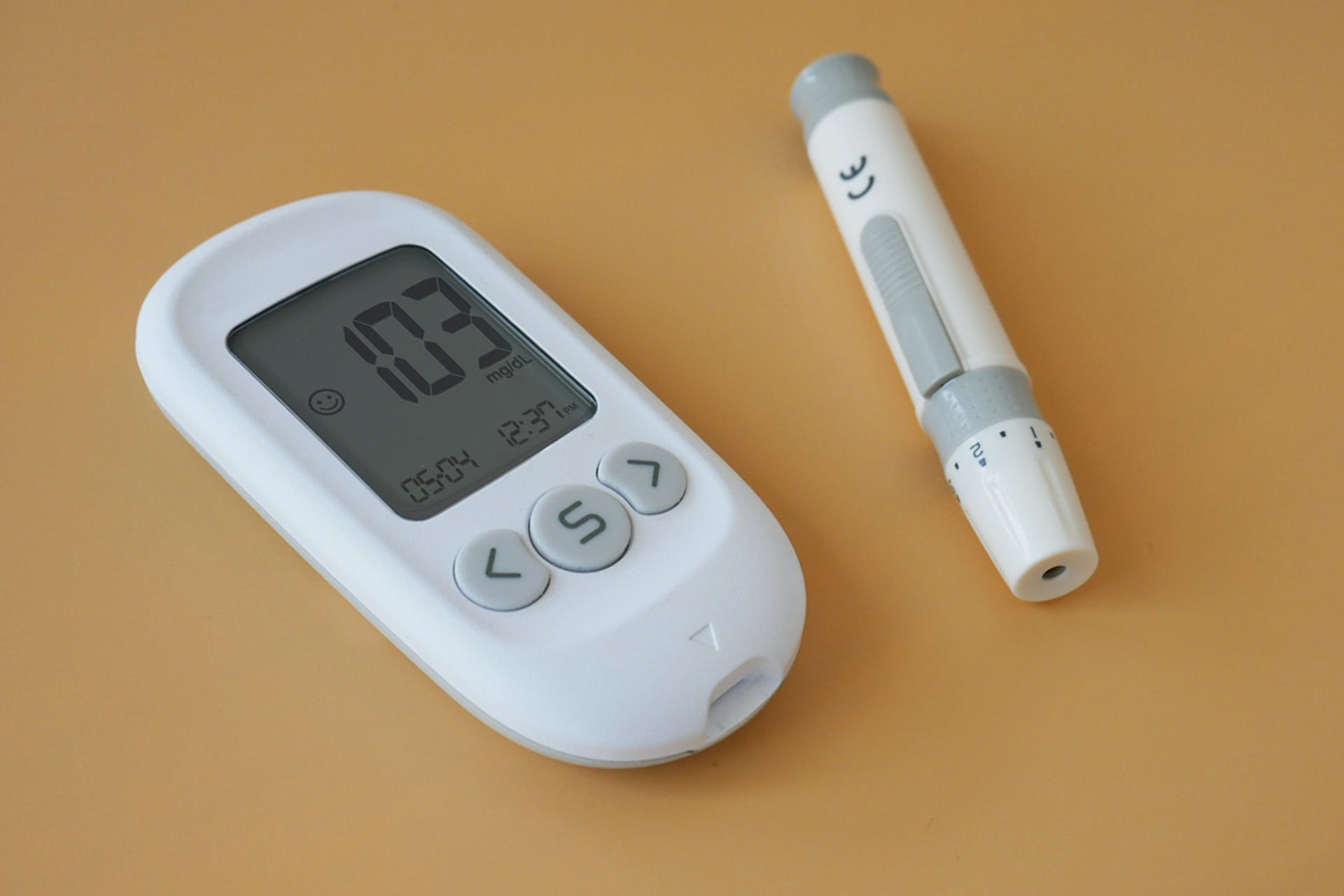
Diabetes is a chronic disease that is divided into two types:
Type 1 diabetes: Caused by insufficient secretion of insulin and usually occurs in younger people.
Type 2 diabetes: Caused by a poor response of cells to insulin and usually occurs in adults.
Whether it is type 1 or type 2 diabetes, high blood sugar is one of its main characteristics.
Long-term high blood sugar increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart disease and stroke.
High blood sugar can damage blood vessel walls, leading to arteriosclerosis and thrombosis.
In addition, high blood sugar can also damage the heart’s nervous system, affect the normal function of the heart, and increase the risk of heart attack.
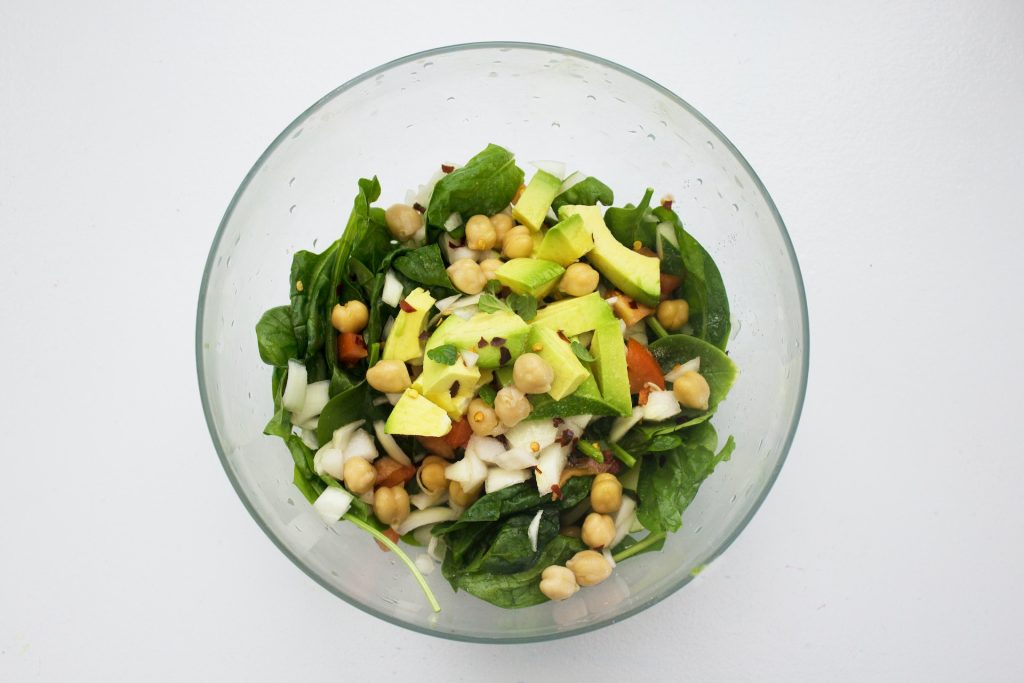

Choose low GI (glycemic index) foods such as whole grains, vegetables and legumes.
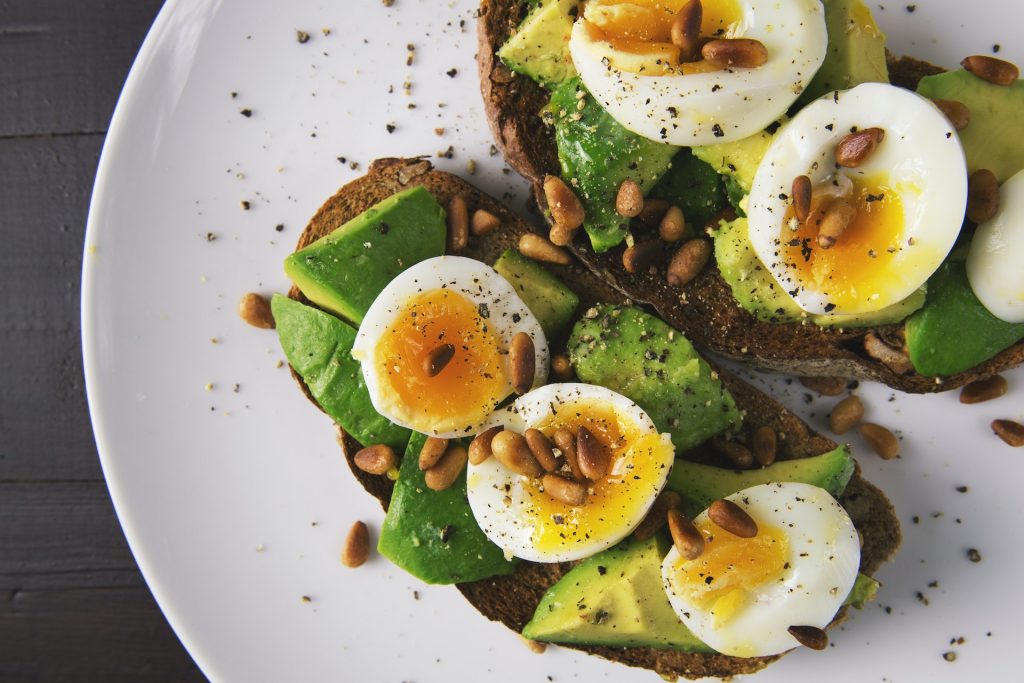

Make sure each meal includes enough protein and healthy fats to help ease blood sugar swings.
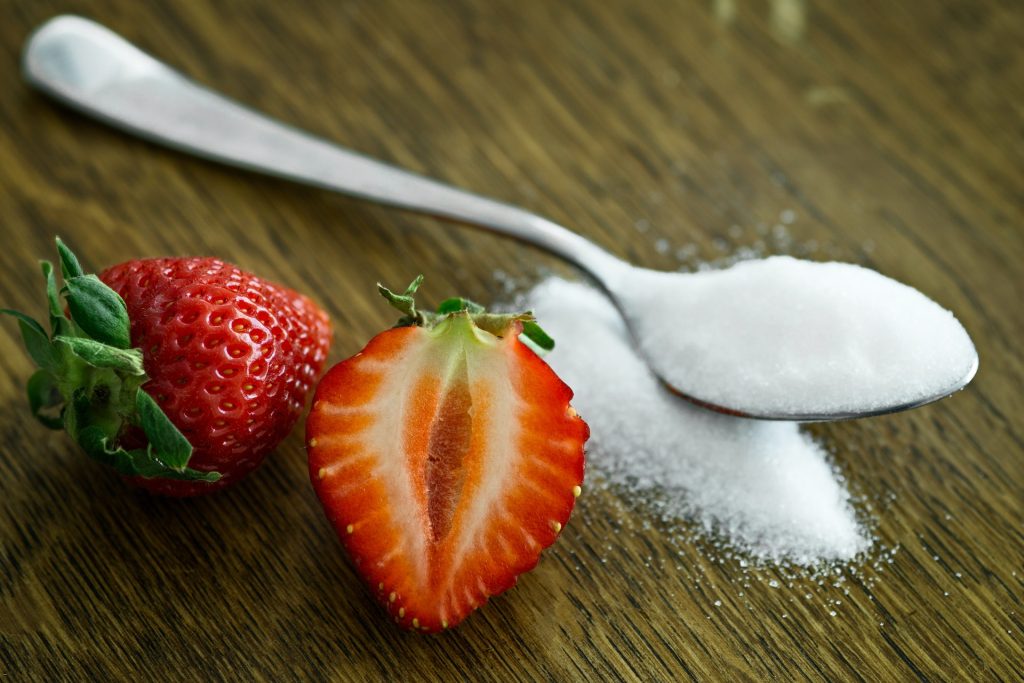

Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks and choose natural sweeteners such as fruit.
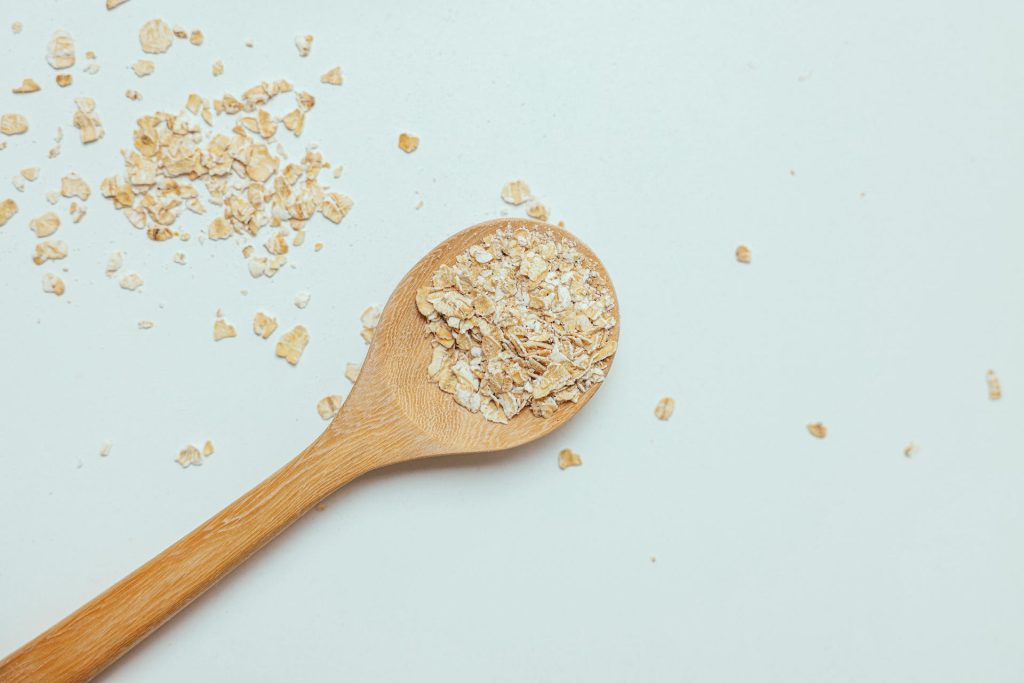

Avoid overeating, especially high-carbohydrate foods.
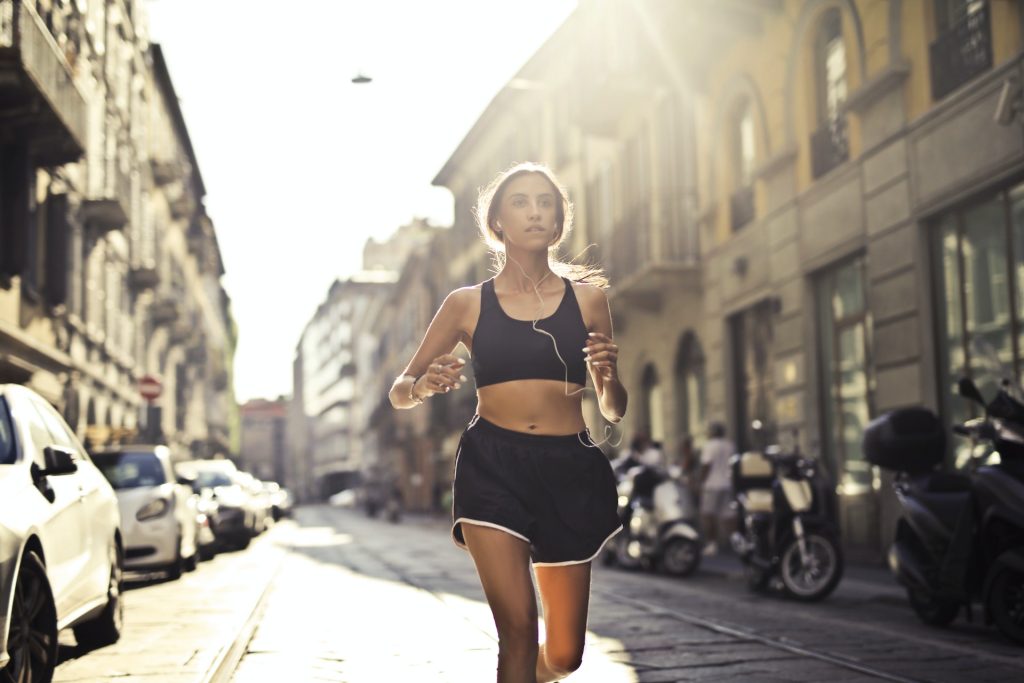

Exercise increases the use of glucose by muscles and helps lower blood sugar levels.
Some effective exercises include aerobic exercise (such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming) and endurance training (such as weight training).
The best time to exercise is usually after a meal, when blood sugar levels are highest.
Follow your doctor’s advice and check your blood sugar levels regularly.
Including healthy eating, moderate exercise, quitting smoking and limiting alcohol, etc.
Check your feet regularly, keep them clean and moisturized, and avoid injuries and infections.
Learn how to deal with stress and avoid the impact of mood swings on blood sugar.